Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) in Africa are governed by local laws, Regional or International legally binding instruments. Currently, there are two Regional IP bodies on the African Continent, namely the African Regional Intellectual Property Organization (ARIPO) and the Organisation Africaine de la Propriete Intellectuelle (OAPI).
The OAPI System
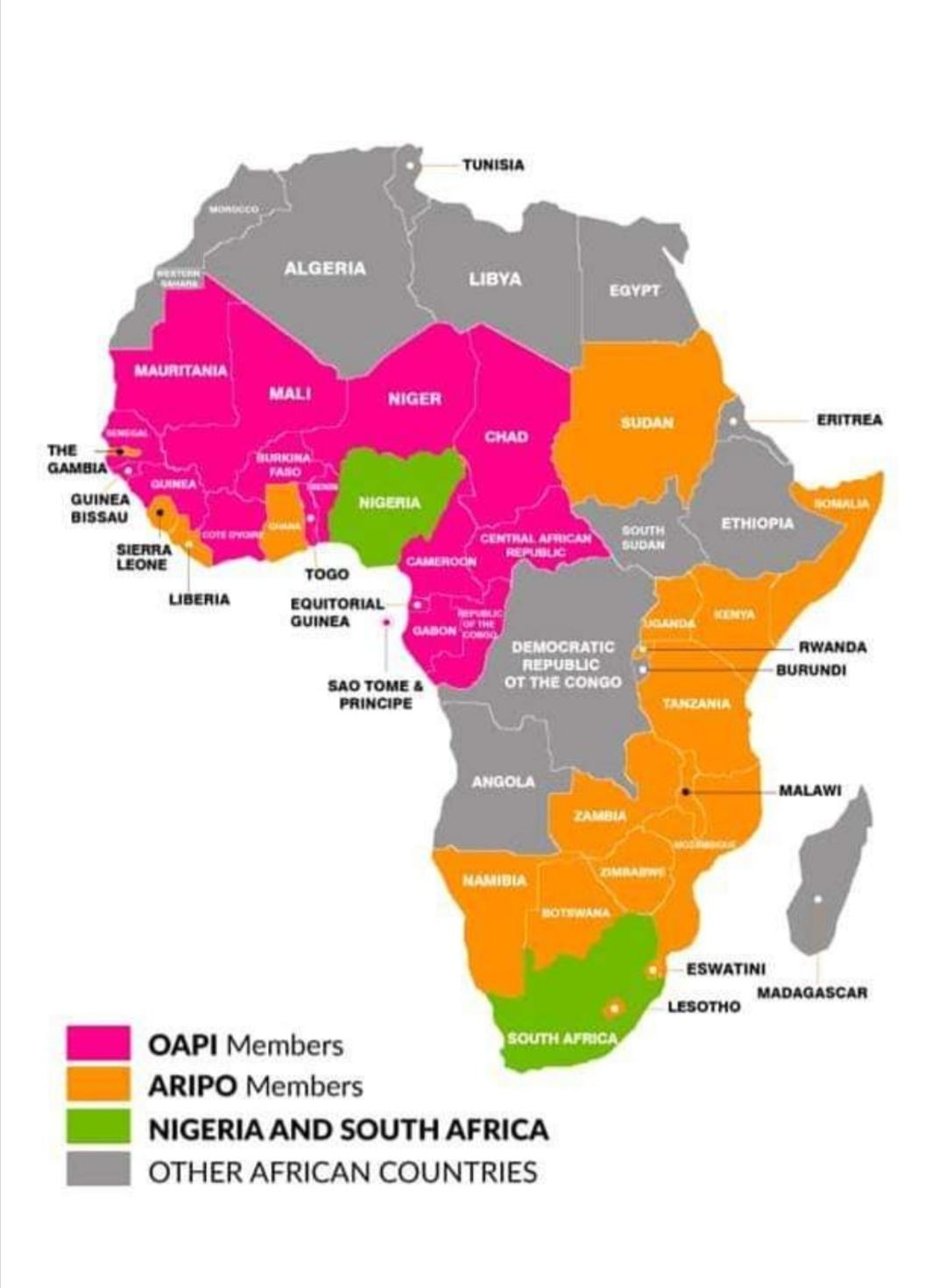
- Headquartered in Yaounde, Cameroon, the member states of OAPI are Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Senegal, Togo and Comoros.
- Among others, the Bangui Agreement which established OAPI, set as part of its responsibilities, to implement and apply common administrative procedure deriving from a uniform system for the protection of industrial property as
well as the provision of international agreements in this field to which the Member States of the organisation have acceded and providing services related to industrial property.
- Through OAPI, rights holders can apply to register patents, trademarks and industrial designs which if successful, affords protection covering the 17 states.
- While OAPI facilitates and maintains these registrations, enforcement in terms of infringement must be handled within the member states concerned.
- Other official actions in respect of the IP rights granted, such as cancellations, oppositions or assignments, are conducted through the OAPI headquarters in
Cameroon.
The ARIPO System
- Headquartered in Harare Zimbabwe, ARIPO comprises of the following member states:
Botswana, The Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Sierra Leonne, Somalia, Sudan, Swaziland, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- Unlike OAPI, ARIPO administers IPRs on behalf of member states and a successful grant for and on behalf of a member state does not mean automatic protection in other states.
- Only 10 out of the 19 member states are parties to the Banjul Protocol which governs trademarks administration in ARIPO.
- Enforcement of IPRs are conducted at the relevant member countries where the infringement occurs.
Other African Countries:
- The remaining African countries individually administer IPRs on a country-to-country basis and the local laws as well as relevant international treaty / convention / agreement apply.
- Enforcement of IP rights from infringement are also managed by the rights holders locally.